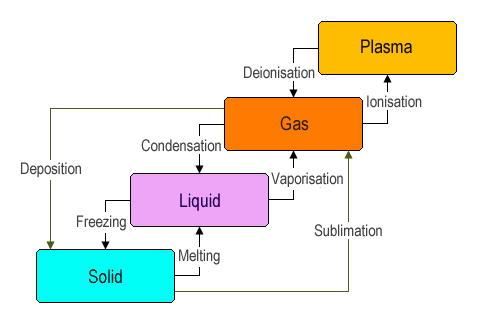
Interconversion of one state of matter to another state of matter is known as phase transition. The three states of matter, i.e. solid, liquid and gas, can interchange into each other under different conditions of temperature and pressure. Let us understand this one by one:
Conversion of solid to
a. Liquids: This process is known as melting. For example, melting of ice cream.
Melting point: It is the temperature at which the solid phase changes to the liquid phase or the temperature at which the solid-liquid state is in equilibrium.
b. Gas: This process is known as sublimation. For example, conversion of solid camphor to vapors.
"Phase transition is a physical process."
Conversion of liquid to
a. Solid: is known as freezing. For example, changing of liquid water to ice.
a. Solid: is known as freezing. For example, changing of liquid water to ice.
b. Gas: is known as vaporization. For example, changing of liquid water to water vapor.
Boiling point: The temperature at which the liquid changes to gaseous state or the temperature at which liquid-gas exist in equilibrium.
Conversion of gas to
a. Solid: is known as deposition.
b. Liquid: is known as condensation.
Latent heat of fusion: The amount of heat energy absorbed or released when a solid change to liquids at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as latent heat of fusion.
For example, when water changes its phase from solid to liquid, a lot of energy is utilized but the temperature does not change. The energy is consumed but no effect on temperature is visible. Hence, the name latent heat (i.e. hidden heat).
Latent heat of vaporisation: The amount of heat energy absorbed or released when a liquid changes to gaseous at its boiling point is known as latent heat of vaporisation.




No comments:
Post a Comment