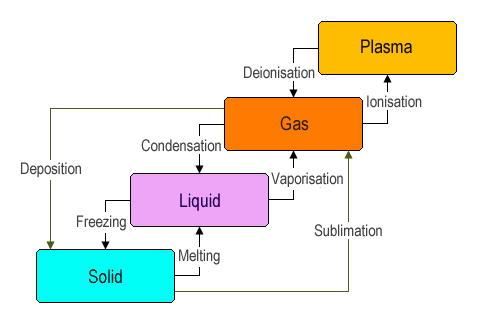
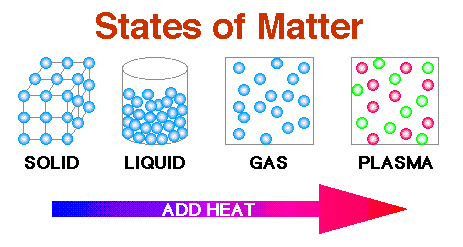
The following are the terms that are used in chemistry very frequently.
Element: a chemical element is a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means. For example, hydrogen, oxygen etc.
Element: a chemical element is a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means. For example, hydrogen, oxygen etc.
Atom: the smallest particle of a chemical element that can exist. For example, the basic unit of hydrogen element is hydrogen atoms. An element has the same kind of atoms.
Compound: A compound is a substance formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together. For example, HCl, NaCl etc.
A molecule of an element: when the same kind of element combines together, they form a molecule of an element. For example, H2, Cl2, O2, S8, P4 etc.
A molecule of a compound: when different elements combine together in a fixed ratio, they form a molecule of a compound. For example, 8g of oxygen combines with 1g of hydrogen to form 9g of water.
Mixture: a substance made by mixing two or more substance together in any proportion. A mixture is of two types.
a. Homogeneous mixture: a mixture which has the same proportion of its components throughout any given sample. For example, alloys.
b. Heterogeneous mixture: a mixture whose proportion vary throughout the sample. For example, mud or sand in water.
a. Homogeneous mixture: a mixture which has the same proportion of its components throughout any given sample. For example, alloys.
b. Heterogeneous mixture: a mixture whose proportion vary throughout the sample. For example, mud or sand in water.
Temperature: it is a measure of the hotness or the coldness of the environment.
Pressure: it is the force exerted by the substance per unit area. The pressure of a gas is the force that the gas exerts on the walls of its container.
P = F÷A
Where, P = pressure
F = force exerted
A = area of cross section
It's SI unit is N/sq. m
Volume: it is a 3-D space enclosed by a closed surface.
V = L × B × H
Where L is the length
B = breadth
H = height of the container.
Its SI unit is the cubic metre.
V = L × B × H
Where L is the length
B = breadth
H = height of the container.
Its SI unit is the cubic metre.
Density: it is a measure of how much stuff an object has in a unit volume.
Density = mass/volume.
Density = mass/volume.
It's SI unit is g/L.
Bond: it is the force holding atoms together. For example, the force between Na and Cl is known as an ionic bond.
" A chemical bond is not a line (as shown in covalent or coordinate bonds), it is a force holding things together."
Physical property: properties that do not change the chemical nature of the matter. For example, melting point, odour, colour, physical appearance, refractive index etc.
Chemical property: properties that change the chemical nature of the matter. For example, chemical reactions.
Mass: it is the amount of matter an object has. It does not change with place or centre of gravity. It is generally taken in kg.
Weight: it is the force exerted on an object due to the acceleration of gravity.
W = mg
Where, W = weight
m = mass of the object
g = acceleration due to gravity ( 9.8m/s2)
W = mg
Where, W = weight
m = mass of the object
g = acceleration due to gravity ( 9.8m/s2)
Chemical equation: it is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and formulae. In this, the reactants are written on the left-hand side and products on the right-hand side.
Example, Cu + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2
Example, Cu + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2
Valency: it is the combining power of an element with other atoms when it forms a chemical compound.
Or, valency is the number of electrons gained or lost in order to complete the octet.
For example, the valency of Na is 1 as it loses 1 electron to attain noble gas configuration while valency of S is 2 as it gains 2 electrons to complete its octet.
Or, valency is the number of electrons gained or lost in order to complete the octet.
For example, the valency of Na is 1 as it loses 1 electron to attain noble gas configuration while valency of S is 2 as it gains 2 electrons to complete its octet.
These terms will be helpful in your studies.